멀티스레딩 동기화란?
멀티스레딩 환경에서 여러 스레드가 동시에 같은 리소스에 접근하려 할 때, 데이터의 일관성과 무결성을 유지하는 것이 매우 중요합니다.
자바 동시성 프로그래밍에서는 뮤텍스(Mutex)와 세마포어(Semaphore) 같은 동기화 메커니즘을 제공하여 이 문제를 해결합니다.
이 글에서는 Java 동기화 기법의 핵심인 뮤텍스와 세마포어의 개념을 설명하고,
실제 Java 코드 예제와 JUnit5 테스트코드로 차이점을 살펴보겠습니다.
🔍 왜 동기화가 필요한가?
- Race Condition 방지
- 데이터 무결성 보장
- 스레드 안전성 확보
- 성능 최적화
뮤텍스(Mutex) 개념과 구현
뮤텍스란?
뮤텍스(Mutex)는 Mutual Exclusion(상호 배제)의 약자입니다.
한 번에 하나의 스레드만이 특정 리소스나 코드 섹션에 접근할 수 있도록 제어하는 Java 동기화 기법입니다.
뮤텍스 동작 원리
리소스에 접근하는 스레드가 뮤텍스를:
- 🔒 잠그고(lock) - 리소스 독점
- ⚙️ 작업을 수행 - 크리티컬 섹션 실행
- 🔓 해제(unlock) - 다른 스레드에게 리소스 반환
핵심: 한 시점에 단 하나의 스레드만 리소스를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Java ReentrantLock 구현
자바에서는 ReentrantLock 클래스를 사용하여 뮤텍스를 구현할 수 있습니다.
Lock 인터페이스의 구현체로, 락의 획득과 해제를 수동으로 제어할 수 있습니다.
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 뮤텍스를 이용한 동기화 예제
* @author JavaDev
* @version 1.0
* @since 2025
*/
public class MutexExample {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int sharedResource = 0;
/**
* 동기화된 리소스 접근 메서드
* @param threadId 스레드 식별자
*/
public void accessResource(int threadId) {
// 자원 진입 시도
System.out.println("🔄 Thread " + threadId + " is trying to access the resource.");
lock.lock(); // 뮤텍스 잠금
try {
// 크리티컬 섹션 진입
System.out.println("✅ Thread " + threadId + " is accessing the resource.");
// 실제 작업 시뮬레이션
sharedResource++;
System.out.println("📊 Shared resource value: " + sharedResource);
// 작업 시간 지연 (로그 관찰용)
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.err.println("❌ Thread " + threadId + " was interrupted");
} finally {
// 자원 사용 완료 및 뮤텍스 해제
System.out.println("🔓 Thread " + threadId + " is releasing the resource.");
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int getSharedResource() {
return sharedResource;
}
}뮤텍스 JUnit5 테스트 코드
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 뮤텍스 동기화 테스트
*/
class MutexExampleTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("뮤텍스로 동시성 제어 테스트")
void mutexConcurrencyTest() throws InterruptedException {
// Given
final MutexExample example = new MutexExample();
final int threadCount = 5;
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
// When
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
executor.submit(() -> example.accessResource(threadId));
}
// Then
executor.shutdown();
boolean finished = executor.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 검증
assert finished : "모든 스레드가 정상적으로 완료되어야 함";
assert example.getSharedResource() == threadCount : "공유 리소스 값이 스레드 수와 일치해야 함";
System.out.println("🎯 최종 공유 리소스 값: " + example.getSharedResource());
}
}
테스트 결과 분석: 하나의 스레드가 완전히 끝나야 다른 스레드가 진입할 수 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
세마포어(Semaphore) 개념과 구현
세마포어란?
세마포어(Semaphore)는 리소스에 동시에 접근할 수 있는 스레드의 수를 제한하는 Java 동시성 제어 메커니즘입니다.
세마포어 동작 원리
- 허가증(Permits) 시스템 사용
- java.util.concurrent.Semaphore 클래스 활용
- acquire() 메서드로 허가증 획득
- release() 메서드로 허가증 반환
- 제한된 수의 스레드만 동시 접근 허용
세마포어 활용 시나리오
- 커넥션 풀 관리
- API 호출 제한
- 파일 다운로드 동시 제한
- 리소스 풀링
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* 세마포어를 이용한 동시 접근 제어 예제
* @author JavaDev
* @version 1.0
* @since 2025
*/
public class SemaphoreExample {
// 동시에 3개의 스레드만 접근 허용
private final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
private volatile int activeThreads = 0;
/**
* 세마포어를 이용한 제한된 리소스 접근
* @param threadId 스레드 식별자
*/
public void accessResource(int threadId) {
try {
// 자원 진입 시도
System.out.println("🔄 Thread " + threadId + " is trying to access the resource.");
// 허가증 획득 시도 (블로킹)
semaphore.acquire();
// 동시 접근 스레드 수 증가
synchronized(this) {
activeThreads++;
System.out.println("✅ Thread " + threadId + " acquired permit. Active threads: " + activeThreads);
}
// 크리티컬 섹션 실행
System.out.println("🎯 Thread " + threadId + " is accessing the resource.");
// 작업 시뮬레이션
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.err.println("❌ Thread " + threadId + " was interrupted");
} finally {
// 동시 접근 스레드 수 감소
synchronized(this) {
activeThreads--;
System.out.println("🔓 Thread " + threadId + " is releasing permit. Active threads: " + activeThreads);
}
// 허가증 반환
semaphore.release();
}
}
/**
* 현재 활성 스레드 수 반환
* @return 활성 스레드 수
*/
public int getActiveThreads() {
return activeThreads;
}
/**
* 사용 가능한 허가증 수 반환
* @return 사용 가능한 허가증 수
*/
public int getAvailablePermits() {
return semaphore.availablePermits();
}
}세마포어 JUnit5 테스트 코드
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 세마포어 동시성 제어 테스트
*/
class SemaphoreExampleTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("세마포어로 동시 접근 제한 테스트")
void semaphoreConcurrencyTest() throws InterruptedException {
// Given
final SemaphoreExample example = new SemaphoreExample();
final int threadCount = 10;
final int maxConcurrentAccess = 3;
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
// When
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
executor.submit(() -> example.accessResource(threadId));
}
// Then
executor.shutdown();
boolean finished = executor.awaitTermination(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long executionTime = endTime - startTime;
// 검증
assert finished : "모든 스레드가 정상적으로 완료되어야 함";
assert example.getActiveThreads() == 0 : "모든 스레드가 완료된 후 활성 스레드는 0이어야 함";
assert example.getAvailablePermits() == maxConcurrentAccess : "모든 허가증이 반환되어야 함";
System.out.println("📊 총 실행 시간: " + executionTime + "ms");
System.out.println("🎯 최대 동시 접근 허용: " + maxConcurrentAccess + "개 스레드");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("세마포어 tryAcquire 테스트")
void semaphoreTryAcquireTest() throws InterruptedException {
// Given
SemaphoreExample example = new SemaphoreExample();
Semaphore testSemaphore = new Semaphore(2);
// When & Then
assert testSemaphore.tryAcquire() : "첫 번째 허가증 획득 성공";
assert testSemaphore.tryAcquire() : "두 번째 허가증 획득 성공";
assert !testSemaphore.tryAcquire() : "세 번째 허가증 획득 실패 (제한 초과)";
System.out.println("✅ tryAcquire 테스트 완료");
}
}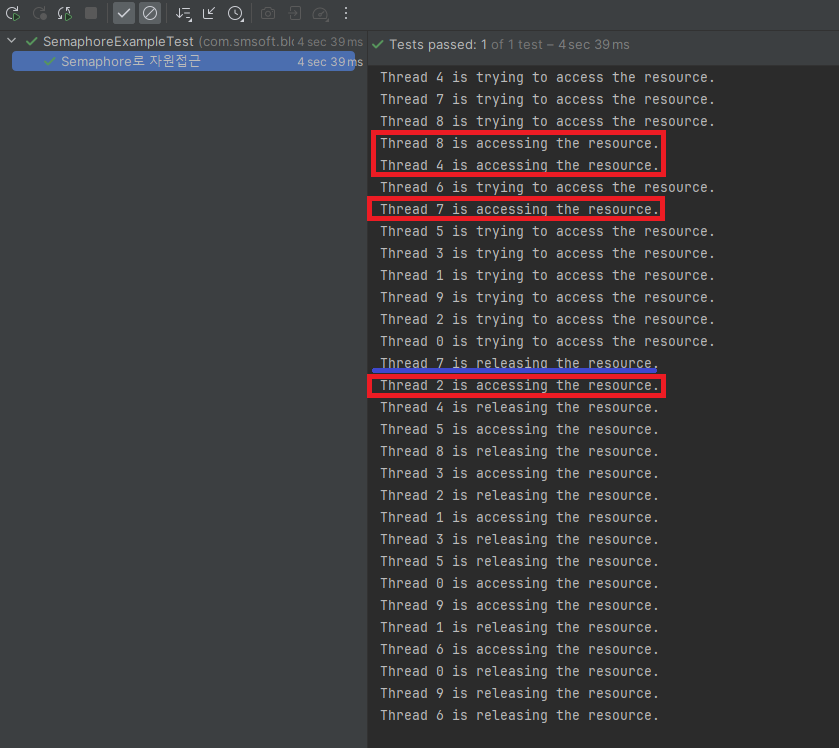
테스트 결과 분석: 최대 3개의 스레드가 동시에 허용되고, 허가증 사용이 완료되면 다음 스레드가 진입할 수 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
뮤텍스 vs 세마포어 비교
📊 상세 비교표
| 구분 | 뮤텍스(Mutex) | 세마포어(Semaphore) |
|---|---|---|
| 동시 접근 스레드 수 | 1개 (독점적) | N개 (제한적) |
| 주요 목적 | 상호 배제 (Mutual Exclusion) | 접근 제한 (Access Control) |
| 메커니즘 | Lock/Unlock | Acquire/Release |
| Java 구현체 | ReentrantLock | Semaphore |
| 사용 사례 | 단일 리소스 보호 | 리소스 풀 관리 |
| 성능 특성 | 순차 처리 | 제한적 병렬 처리 |
| 데드락 위험 | 높음 | 상대적으로 낮음 |
🎯 언제 무엇을 사용할까?
뮤텍스를 사용해야 하는 경우:
- 단일 공유 리소스 보호
- 데이터 무결성이 절대적으로 중요한 경우
- 순차적 처리가 필요한 작업
- 계좌 잔액 업데이트, 파일 쓰기 등
세마포어를 사용해야 하는 경우:
- 제한된 리소스 풀 관리
- 동시 접근 수 제어가 필요한 경우
- 성능 최적화를 통한 병렬 처리
- 데이터베이스 커넥션 풀, 스레드 풀 등
실무에서의 활용 팁
🔧 성능 최적화 팁
1. 공정성(Fairness) 설정
// 공정한 락 - FIFO 순서 보장
ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock(true);
Semaphore fairSemaphore = new Semaphore(3, true);2. 타임아웃 설정
// 타임아웃이 있는 락 시도
if (lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
try {
// 크리티컬 섹션
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
// 타임아웃 처리
}3. 논블로킹 시도
// 즉시 실패하는 시도
if (semaphore.tryAcquire()) {
try {
// 작업 수행
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
🚨 주의사항과 베스트 프랙티스
⚠️ 주의사항
- 데드락 방지: 락 순서 일관성 유지
- 리소스 누수 방지: finally 블록에서 반드시 해제
- 성능 고려: 불필요한 동기화 최소화
- 예외 처리: InterruptedException 적절한 처리
✅ 베스트 프랙티스
// 좋은 예시
lock.lock();
try {
// 크리티컬 섹션
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 반드시 해제
}
// 나쁜 예시 (절대 하지 말 것)
lock.lock();
// 작업 수행
lock.unlock(); // 예외 발생 시 해제되지 않음📈 성능 모니터링
/**
* 동기화 성능 모니터링 유틸리티
*/
public class SyncMonitor {
private long waitTime = 0;
private long executionTime = 0;
public void measureLockPerformance(Runnable task) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
lock.lock();
long lockAcquired = System.nanoTime();
try {
task.run();
} finally {
long end = System.nanoTime();
waitTime += (lockAcquired - start);
executionTime += (end - lockAcquired);
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 통계 정보 출력
public void printStats() {
System.out.println("대기 시간: " + waitTime / 1_000_000 + "ms");
System.out.println("실행 시간: " + executionTime / 1_000_000 + "ms");
}
}🎯 결론
뮤텍스(Mutex)와 세마포어(Semaphore)는 Java 멀티스레딩에서 동시성을 제어하는 핵심적인 동기화 메커니즘입니다.
📋 핵심 요약
- 뮤텍스: 상호 배제를 통한 단일 리소스 독점 제어
- 세마포어: 제한된 수의 스레드가 동시에 리소스 접근 허용
- 올바른 선택: 요구사항에 따른 적절한 동기화 기법 선택이 중요
- 성능 고려: 동시성과 안정성의 균형점 찾기
이러한 Java 동기화 기법을 통해 멀티스레딩 환경에서 데이터 일관성과 무결성을 보장하면서도 최적의 성능을 달성할 수 있습니다.
실무에서는 요구사항을 정확히 분석하고, 적절한 동기화 메커니즘을 선택하여 안정적이고 효율적인 멀티스레드 애플리케이션을 개발하시기 바랍니다.
📚 참고자료
공식 문서
추가 학습 자료
💡 이 글이 도움이 되셨다면 공유해주세요! 멀티스레딩과 관련된 더 많은 Java 개발 팁이 궁금하시다면 댓글로 알려주세요.
'컴퓨터 과학(CS)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| RSA 암호화 알고리즘의 원리와 적용 사례 (0) | 2025.01.25 |
|---|---|
| IPv4와 IPv6 완벽 가이드: 전환 전략부터 실무 적용까지 (0) | 2025.01.25 |
| 시스템 콜 완벽 가이드: 기본 개념부터 성능 최적화까지 (1) | 2025.01.24 |
| 캐시와 쿠키의 차이점: 성능 및 보안 비교 완전 가이드 (3) | 2025.01.22 |
| HTTP 상태 코드: 자주 사용되는 10가지 코드 정리 (3) | 2025.01.22 |



